

| Inquiry | Bearing Designation | Dimension(mm) | Basic load ratings (kN) | Speed ratings(rpm) | Weight | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | D | B | Cr | Cor | Grease | Oil | (Kg) | |||
| QJ307 | - | 80 | 21 | 53.2 | 37.2 | 6000 | 8000 | 0.57 | ||
| QJ6208-2RSC3 | 40 | 80 | 18 | 1.1 | 44.3 | 27.2 | 4500 | 0.366 | ||
| QJ010MB.402C | 50 | 80 | 16 | 1 | 33.2 | 24.4 | 9000 | 0.25 | ||
| QJ6010-2RS | 50 | 80 | 16 | 1 | 33 | 24.4 | 4700 | 0.25 | ||
| QJ208 | - | 85 | 18 | 40.5 | 37.0 | 6700 | 9000 | 0.391 | ||
| QJF309 | - | 90 | 25 | 55.5 | 50.2 | 4800 | 6300 | 0.923 | ||
| QJF210 | 50 | 90 | 20 | 41.8 | 40.2 | 5000 | 6700 | 0.514 | ||
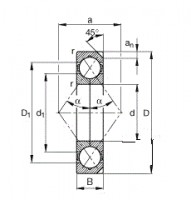
Angular contact ball bearings provide significant advantages in precision, axial load capacity, and reduced friction compared to radial bearings. Their ability to support both radial and axial loads in a single direction makes them ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and efficiency, such as machine tool spindles and automotive systems. The contact angle between the balls and raceways minimizes friction, resulting in lower heat generation and enhanced durability. Angular contact bearings are versatile in arrangement, allowing for optimized load distribution and operational flexibility. These qualities collectively contribute to longer service life, reduced maintenance, and improved performance across a wide range of industrial applications.